Ever used Amazon’s Alexa, or Google Home, or Microsoft’s Cortana? If you have any of those or have an idea of what they are, you already have a slight idea about Artificial Intelligence. All of these apps are personalized apps which mold and evolve when you interact with them.
The level of personalisation is so high that Google Home provides you with a feature wherein Google Home would detect who you are by your voice and would show you results based on your preferences. For example, if two roommates live in a house, Google Home would maintain separate records for both of them so that when one of them asks for their schedule for the day, Google Home knows which schedule to give.
All of it is the work of Artificial Intelligence. Artificial Intelligence can be seen as a means to see natural human intelligence, at some level, in computers. This is done through codes which have the ability to manipulate all by themselves. These codes don’t need humans to tell them everything and can think for themselves to an extent. They enable the developers to work more freely without having to develop codes for everything new that happens to the device/code.
While there have been a lot of great advancements in the field of AI recently, it isn’t exactly a new field. In fact, what we call AI now has its first working dating back to 1943 when McCullouch and Pitts made a formal design for the Turing-complete “artificial neurons”. Pretty old, eh? The field has been making improvements ever since and has finally managed to reach a level of which we can say that the future is now.
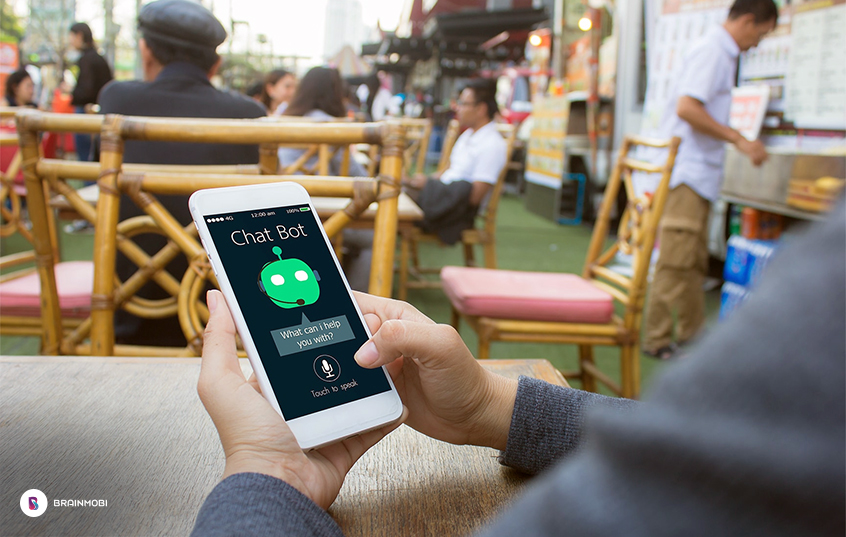
AI is not limited to voice recognition and interactions based on it. There are many chatbots too with which you can interact without even getting to know it is a bot. These bots are designed in such a way that they let you interact with them like a human would. Whenever you type send them a message, your message is broken down into tags. These tags and their context are understood by the bot using special algorithms written down by the programmers. Now that the bot knows what you wish to say, it responds with whatever response fits best.
Interactions via voice, however, are more intuitive and easier to use. The process through which the application understands and responds to your voice is similar to how the chatbots work. Your voice is first deconstructed into a language understandable by the application. Once the application understands what you are saying, it generates a response to what you are saying.
With all of these features, there is no limit to personalisation of mobile apps. In many cases, your app knows more about you than you do. The apps collect data about you that helps in making it more personalised. They know when you wake, and when you sleep, so if there are any changes in your sleeping patterns, the apps can tell you about it. They can sense your mood and respond accordingly. Moreover, they sound a lot more human-like than you would expect from a machine.
BrainMobi is a leading mobile app development company. We have a team of top mobile app developers who work constantly for our clients to get what they require out of us. If you need your app to be developed by mobility experts, contact us at sales@brainmobi.com.
If you found the blog helpful, let us know in the comments below!